Digital Fabrication Skills
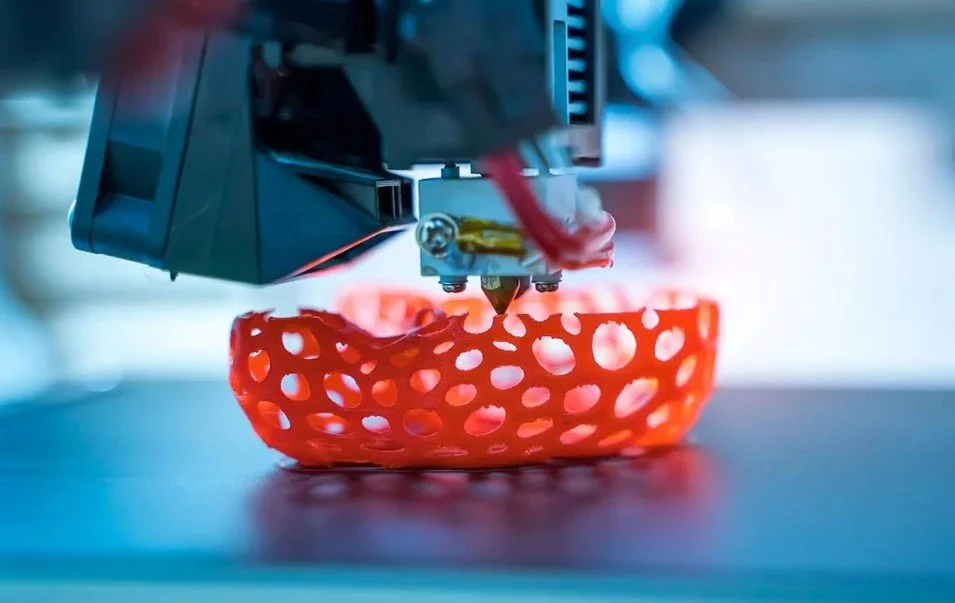
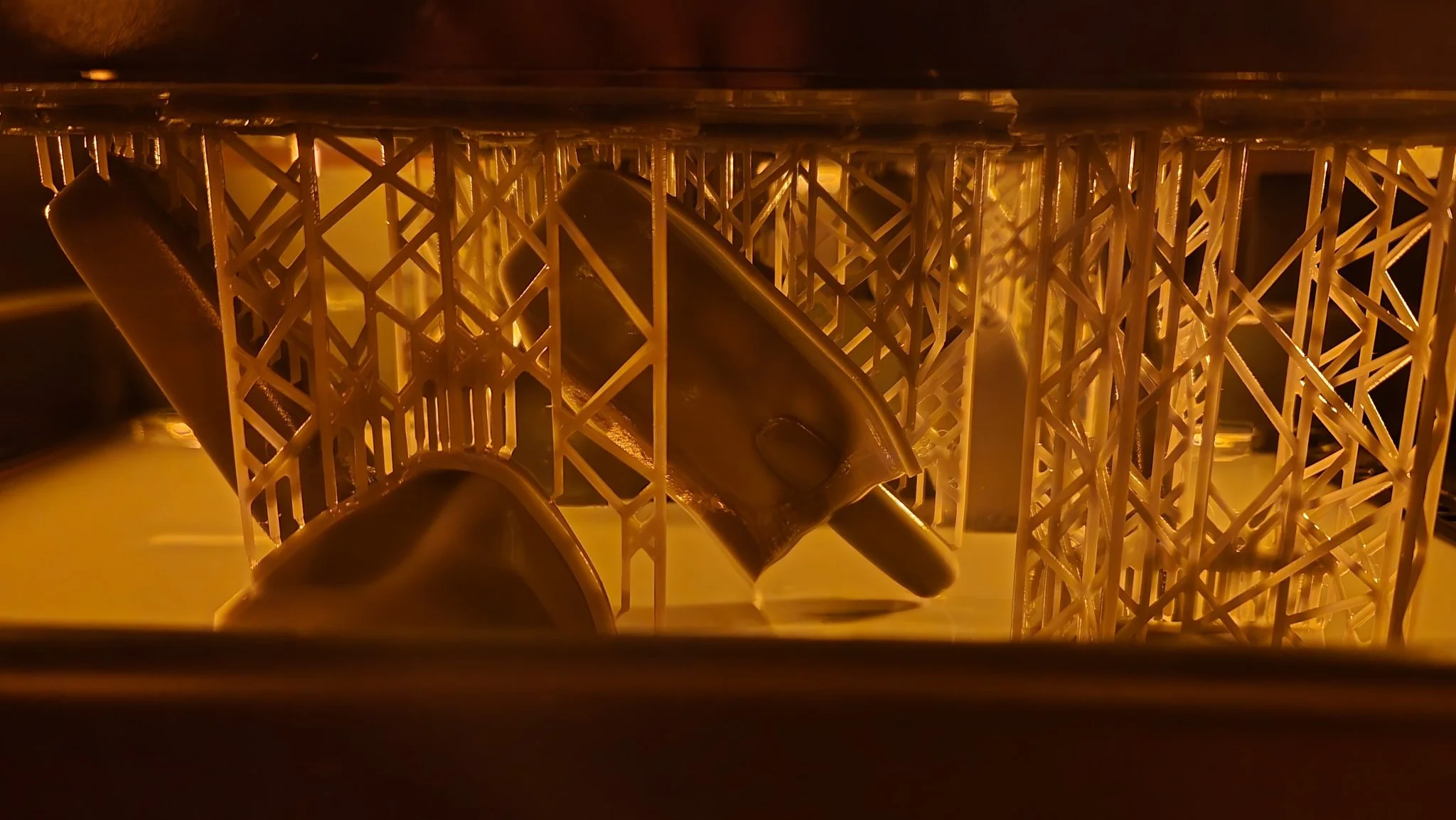
Digital fabrication is the design and manufacturing workflow where digital data directly drives manufacturing equipment to form various parts. It ranges from designing a virtual model on CAD software, to inputting parameters and settings specific to an automated tool. The manufactured parts based on the tool path data collected sometimes requires a form of finishing to achieve their final properties and look before they’re ready to use.
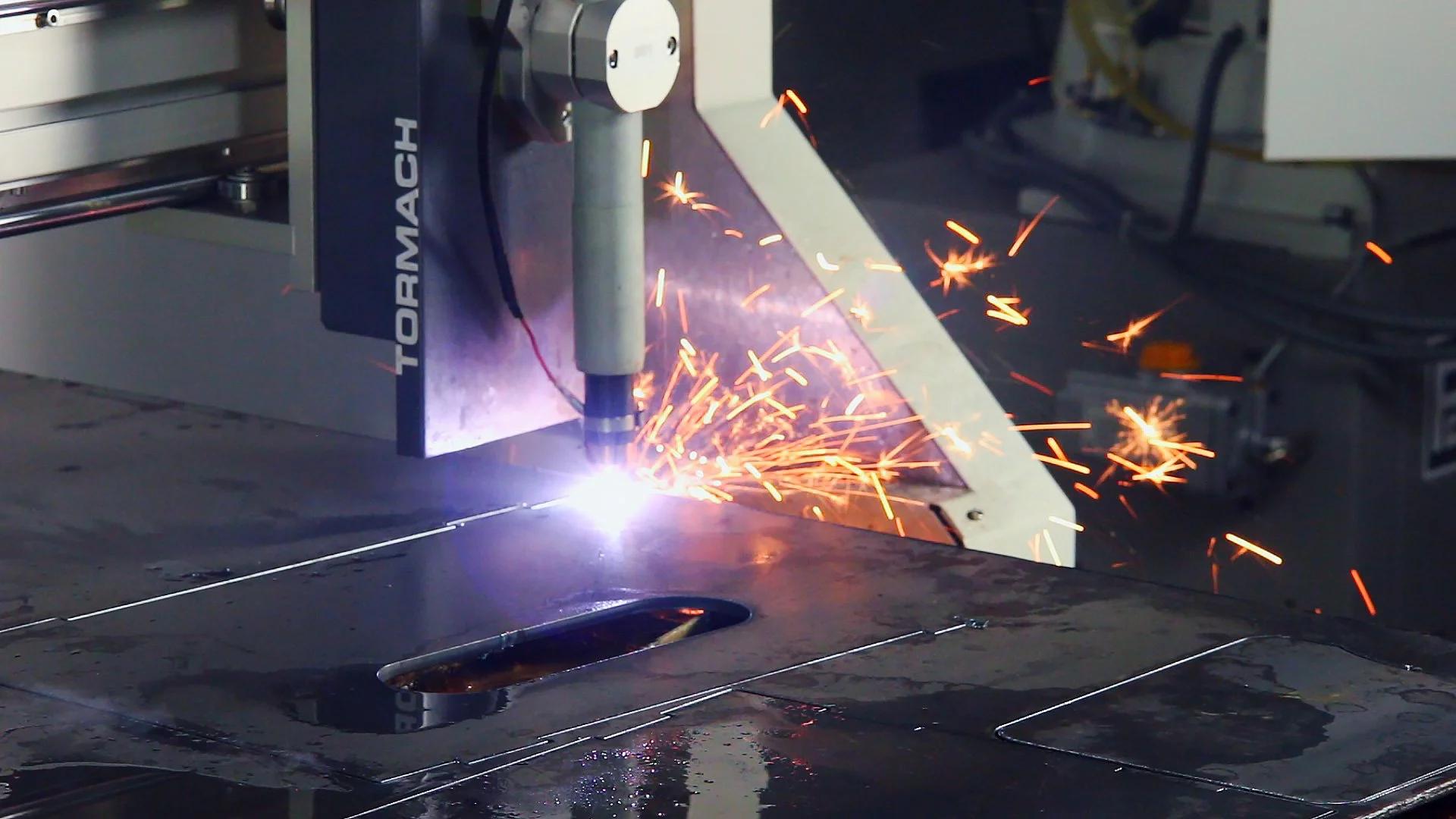
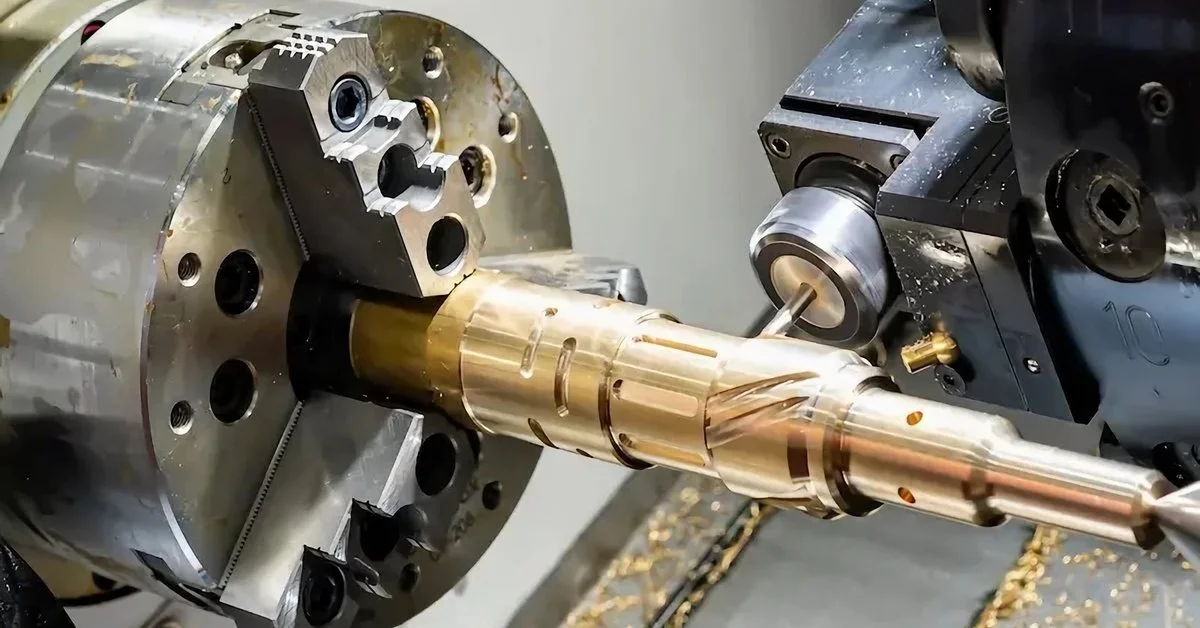
CNC Machining
CNC machining is well known for the ability to cut through tougher materials and create more precise features and finishes. It’s also helpful when you’re working on larger-scale projects or need to manufacture components quickly.
3-Axis Milling
Using a CNC milling machine that spins the cutting tool against a stationary workpiece. It uses primarily square or rectangular bar stock to produce components. This may include rapid prototyping in a range of plastics, metals, and other materials, or precision machining at industry standards.
2-Axis Turning
Using a CNC lathe that rotates the workpiece against a cutting tool. It uses primarily round bar stock for machining components. A turret with tooling attached is programmed to move to the raw material and remove material to create the programmed result.